instructions
Have you ever had many students query why they got a certain score on an assignment?
Have you noticed that your students need to know what is expected of them when performing a task?
Do you find it challenging to provide feedback to all students on an assignment?
The solution might be to use a scoring rubric…
Search the various scoring rubric categories at the site, then choose the most appropriate category and format that achieves the objectives of the assignment to be evaluated.
What are scoring rubrics?
Instruments used for evaluating academic assignments to determine students’ performance levels according to specific criteria in view of learning outcomes.
*Criteria: The main factors according to which the student's work is evaluated.
Why use scoring rubrics?
For students:
- Clarifies outcome expectations for the assignment to be evaluated.
- Helps them understand why they received a certain score for an assignment.
- Keeps the students’ efforts focused on completing an assignment in line with clearly defined expectations.
- Helps improve the learning process.
- It can be considered as self-assessment for the student.
For teachers:
- An effective way to focus on students' work.
- Helps classify tasks more consistently.
- Saves time grading in the long and short term.
- Helps reduce the number of meetings with students to explain obtained scores.
- Helps provide a clear and specific perception of students' strengths and weaknesses.
- Helps facilitate fair evaluation when there is more than one corrector
The design of the scoring rubric varies in terms of the criteria and levels
depending on the targeted learning outcomes
|
Scoring rubrics are used when correcting students' subjective work (such as research papers, projects, portfolios, e-participation, and presentations).
Are scoring rubrics used in objective assessment (such as multiple-choice question)? : No |
How do you choose a scoring rubric model?
● Ensure that the scoring rubric model fits the objectives of the task to be evaluated.
● Review the estimated percentage for each criteria and adjust it to suit the objectives of the task to be evaluated. The estimated percentage in each model is proposed according to the importance of each criterion.
● Some models include additional criteria that you can use but avoid exceeding 8 criteria so that the evaluation process does not become difficult.
Effective uses of scoring rubrics:
Attach to assignment: self-assessment (formative assessment)
Attach to assignment: Peer assessment (formative assessment)
Attached to the assignment and used by the course instructor for assessment (final assessment)
Types of scoring rubrics:
- Analytical: The various criteria are clarified for each task and scores are assigned to each criterion.
- Comprehensive: The general characteristics of the task are explained, and one grade is assigned to the whole task.
| This website only provides samples of analytical scoring rubrics |
Advantages of analytical scoring rubrics:
- Helps accurately identify the student's strengths and weaknesses
- Provides detailed scoring options.
- It can be used in the formative assessment process.
- Helps in developing the learning process.
- Appropriate for assessing tasks that include sub-tasks
Analytic scoring rubric components:
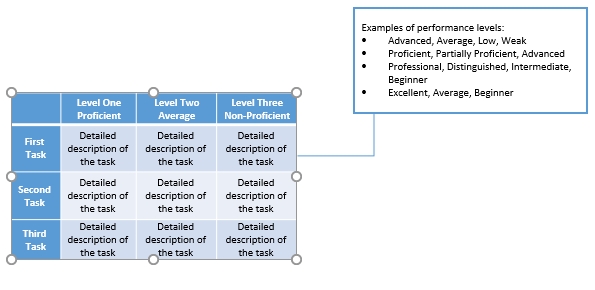
|
If you have never used a scoring rubric, it would be a good idea to follow some steps to make sure that it is a good fit for the task you want to evaluate: ✔ Try the scoring rubric on some students' previous work. ✔ Discuss the adjustments you made to the scoring rubric with your peers. ✔ Show your students the rubric and explain the criteria and performance level descriptions |
Guidelines for designing scoring rubrics:
Scoring rubrics : take a lot of time to design and review, but in return save time and ensure quality during the evaluation process
- Determine the purpose of designing the scoring rubric; what do you want to
measure?
- Determine scoring rubric criteria according to the targeted learning outcomes.
- Determine the number of scoring criteria which should be no less than (3) and
not more than (7). Because if the criteria are below or exceed this limit, the
evaluation process will be inaccurate.
- Determine the number of performance levels which should be no less than (3)
and not more than (5). Because if the levels are below or exceed this limit, the
evaluation process will be inaccurate.
- Determine performance levels by numeric (1-2-3-4) or written (excellent, good,
acceptable, poor) classification.
- Describe the knowledge, skills and behaviours required to perform the task for
each criterion so that they are consistent across levels.
- Review performance level descriptions for each criterion to ensure its
measurability.
References
- https://teaching.uwo.ca/teaching/assessing/grading-rubrics.html
- https://teaching.berkeley.edu/resources/assessment-and-evaluation/design-assessment/rubrics
- https://www.quickrubric.com/about/tips-to-writing-a-strong-rubric
- https://tll.mit.edu/teaching-resources/assess-learning/how-to-use-rubrics/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wPNRhsADPzw&t=5s
